# Waterfall Model
It is a sequential framework that divides software development into predefined phases. Each one must be completed before the next one can begin, with no overlap between phases.
Each stage is structured to carry out a specific activity during the SDLC phase.
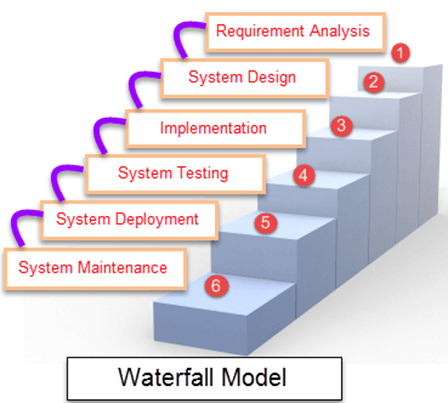
# Stages of the Waterfall Model
Business Requirement Gathering Phase: Gathering as much information as possible about the details and specifications of the software desired by the client.
Design Phase: Planning the programming language to be used, the database, etc. It should fit the project, as well as high-level functions and architecture.
Construction Phase: After the Design, we proceed to actually build the software code.
Testing Phase: Afterward, we test the software to verify that it has been created according to the specifications provided by the client.
Implementation Phase: It implements the application in the designated environment.
Maintenance Phase: Once the system is ready for use, it may be necessary to change the code later depending on user requests.
# When to Use the Waterfall Model?
It can be applied when:
- Requirements do not change constantly;
- The application is not overly complex;
- The project is short;
- Business rules are clear;
- The environment is stable;
- Technology and tools used are not dynamic but stable;
- Resources are available and directed;
# Advantages of the Waterfall Model
- Before the next development phase, the previous one must be completed.
- Suitable for smaller projects with well-defined requirements.
- Quality Assurance (verification and validation) tests should be applied before completing each stage.
- Documentation development is done at each stage of the SDLC.
- The project is entirely dependent on the team, with minimal customer involvement.
- Any changes to the software are made during the development process.
# Disadvantages of the Waterfall Model
- Errors can only be fixed in the next stage.
- Not suitable for complex projects where requirements change constantly.
- The testing period only occurs in the later stages of the development process.
- Documentation takes up a significant amount of developers' and testers' time.
- Valuable customer feedback cannot be included in the ongoing development process.
- Small changes or errors that arise in the finished software can lead to major problems.